High Phosphate Wastewater
High phosphate wastewater from municipal plants reduced by 99.6% using EPT EOX Solution
The Situation
Controlling phosphorous discharged from municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plants is a key factor in preventing eutrophication of surface waters. Phosphorous is one of the major nutrients contributing in the increased eutrophication of lakes and natural waters. Its presence causes many water quality problems including increased purification costs, decreased recreational and conservation value, loss of livestock and the possible lethal effect of algal toxins on drinking water.
Phosphate removal is currently achieved largely by chemical precipitation, which is expensive and causes an increase of sludge volume by up to 40%. An alternative is the biological phosphate removal (BPR), however this is expensive and not conducive to colder climates.
The Solution
Ground Effects EOX solution effectively treats phosphates and other contaminants to below discharge criteria. The EOX technology is scalable, with a small footprint and low operating costs. The EOX module can be easily integrated into existing plants or as a stand alone system.
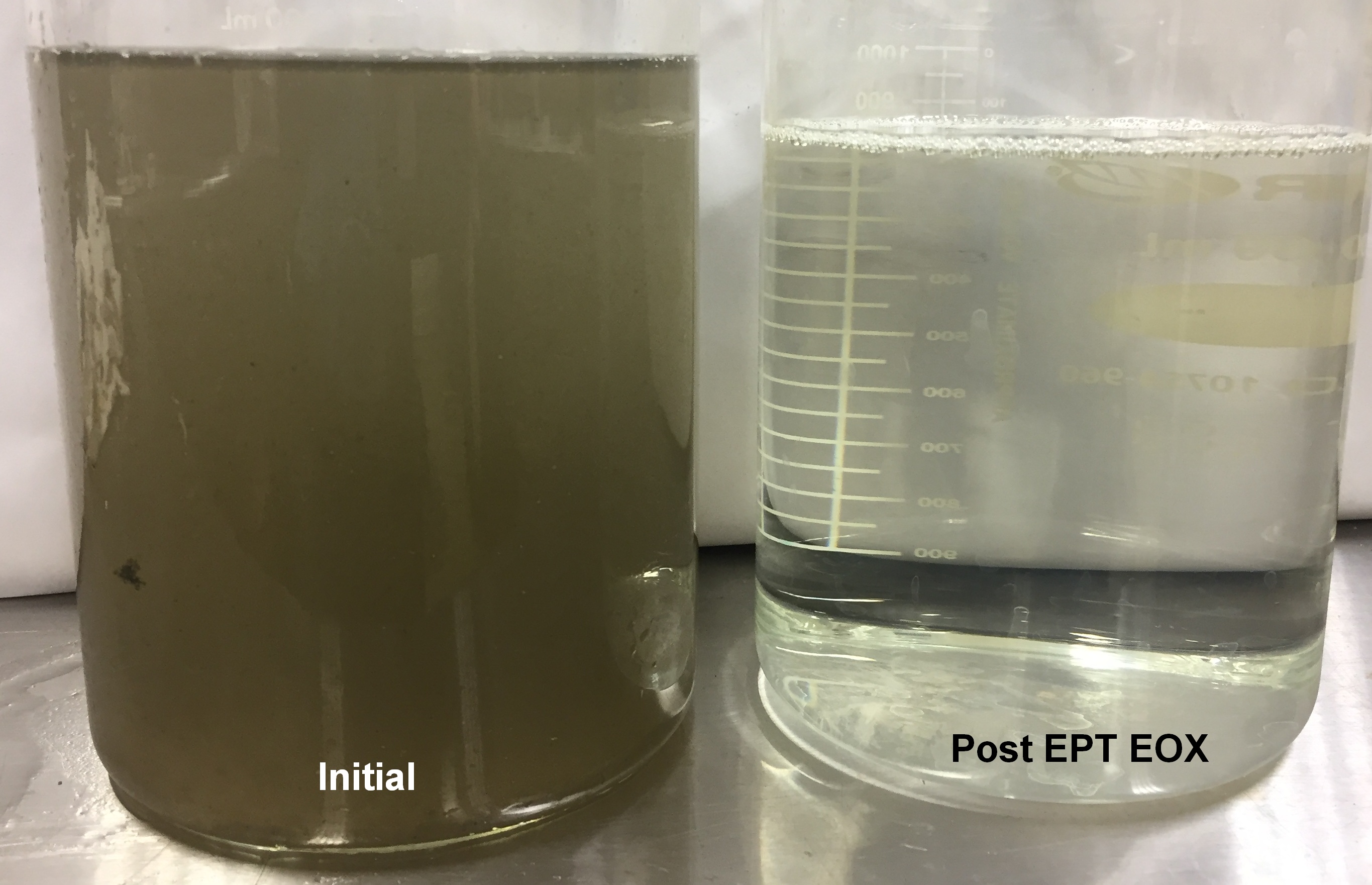
The Results
GEE uses powerful electrocoagulation technology with ozone as a catalyst creating a highly reactive environment where contaminants are broken down and can be easily removed. This significantly reduces or eliminates the use of chemicals, as well as driving down operation and maintenance costs.
High Phosphate Municipal Waste Water
| Parameter | Initial | Post EPT EOX |
|---|---|---|
| Total Phosphorous | 245.04 mg/L | 0.85 mg/L |
| Ortho Phosphorous | 231.46 mg/L | 0.56 mg/L |
