Pneumatic Fracturing System
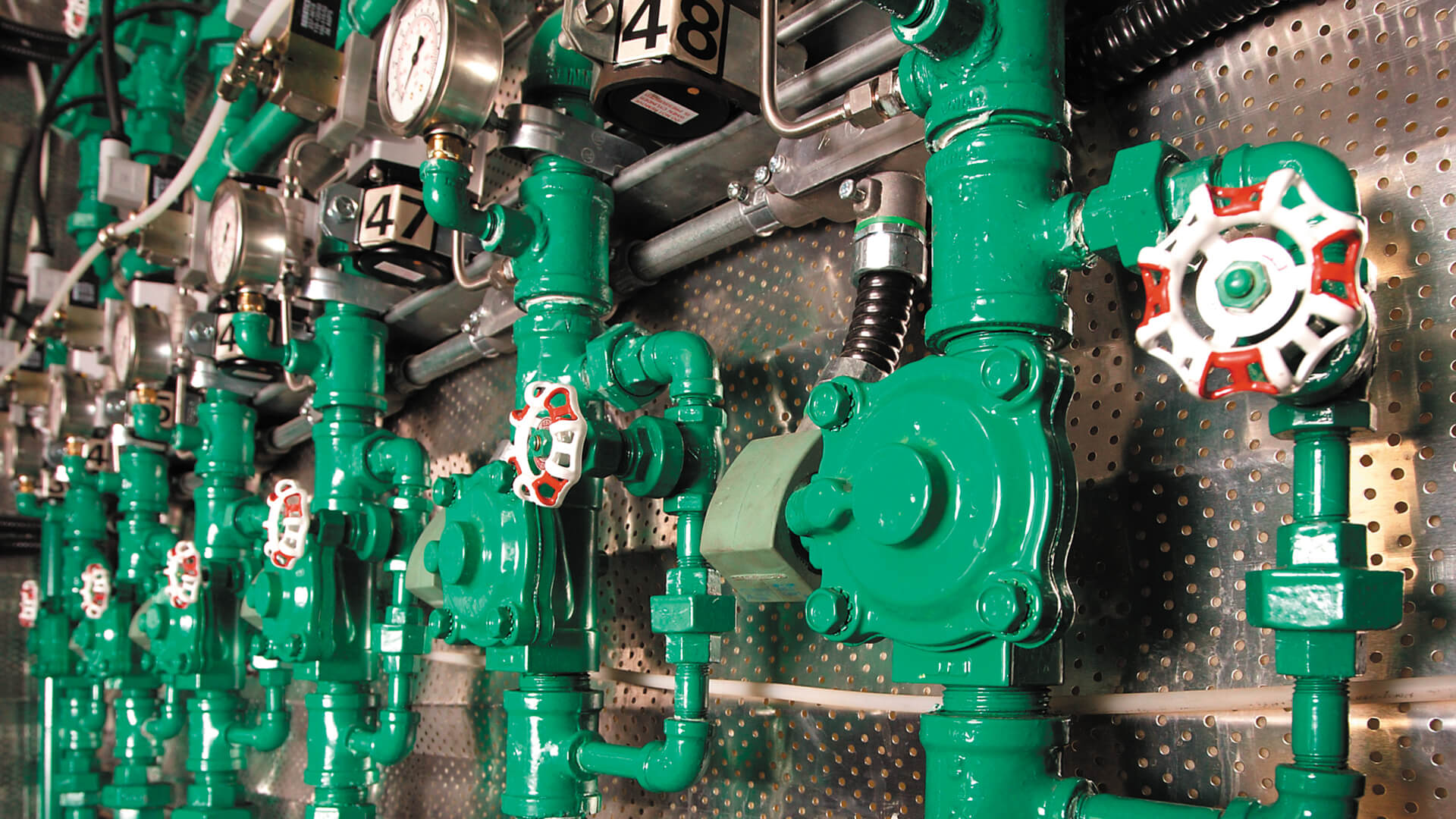
A Multi-Phase Extraction (MPE) Enhancement Technology
The GEE Pneumatic AirLift System (PALS) is a Multi-Phase Extraction (MPE) enhancement technology. When used with an MPE system, the PFS adds significant advantages. Designed to pneumatically fracture tight soils such as clay, the GEE PFS causes fracturing by injecting air (or gases) at a pressure exceeding the natural strength and in situ stresses already in the formation, thus creating more pathways for our MPE system to use. The result is increased efficiency, reduced remediation time and reduced costs.
Applications
- In situ
- Drilling Waste Sites
- Other spills including flowline/pipeline breaks
- Upstream Oil and Gas Industry including refineries, oil and gas drilling sites, oil and gas battery sites, flare pits and other spills
- Downstream Oil and Gas Industry including gas stations and bulk fuel storage facilities
- Retired gas stations, fuel/refinery sites, spills
- Former Manufactured Gas Plants (FMGPs)
- Asphalt Plants
Sectors
Problems Solved
The Science Behind the PFS
The low permeability of clays and other tight subsurface formations is a limiting factor in the success of Multi Phase Extraction (MPE), air sparging and other processes. With this limitation, substantial removal of contaminants may be long and costly.
GEE’s PFS is an enhancement technology that increases the efficiency of MPEs and other technologies in difficult-to-treat soil conditions. With pneumatic fracturing, pressurized air is injected through wells to develop fractures in low permeability and over-consolidated sediments. The new passageways increase extraction efficiencies by increasing contact between contaminants adsorbed onto soil particles and the extraction medium. Essentially, it acts like a push/pull system by increasing the differential pressure. This enhanced and secondary fracture network increases the permeability of the soil to liquids and vapors and accelerates the removal of contaminants.
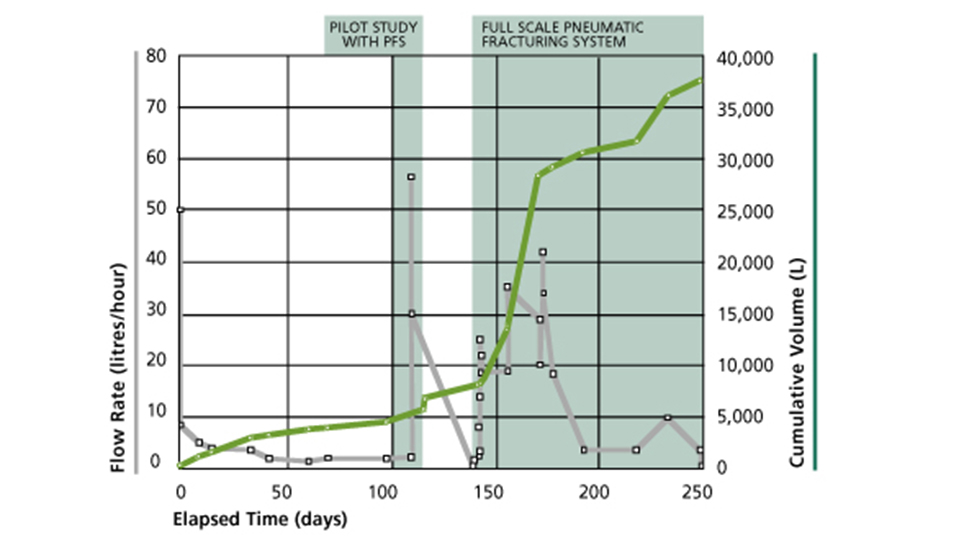
Features

Decreased Cost and Time
The PFS speeds up the MPE process entirely by creating more secondary pathways for the water and vapor. This means increased removal rates by an order of magnitude over MPE usage alone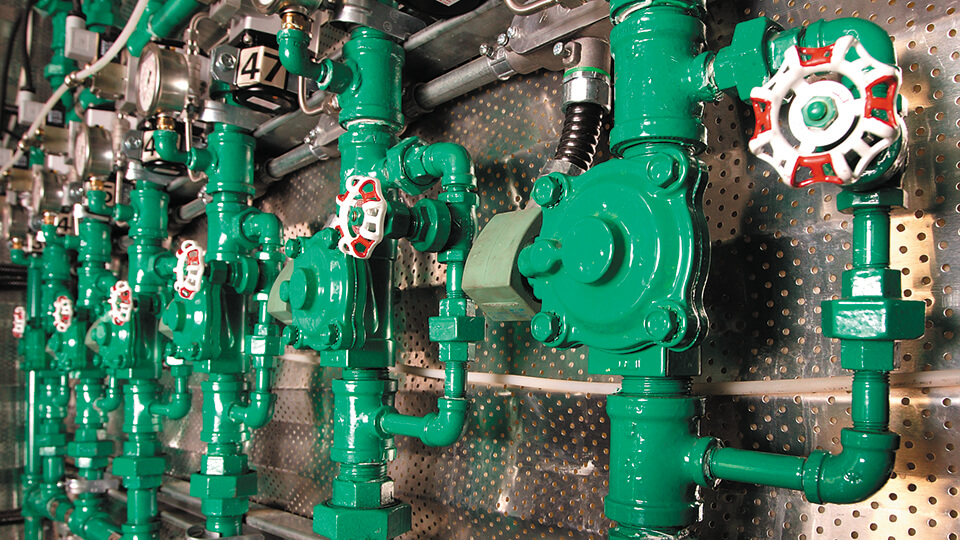
Increased ∆ dp
Increased mean pore diameter (dp) allows for more water vapor and air to flow through the soil and speed up the remediation process.
Enhanced Airflow and Volatilization
With the GEE PFS system increases airflow and the volatilization of contaminants for faster and more effective extraction.
